Breast adipose tissue‐derived extracellular vesicles from obese women alter tumor cell metabolism
4.8 (686) In stock


Obese adipose tissue extracellular vesicles raise breast cancer cell malignancy in: Endocrine-Related Cancer Volume 27 Issue 10 (2020)

Adipose stromal cells (ASCs) possess distinct biologic properties as a

Schematic summary for the novel circulatory miRNAs in patients

Dr. Paul Paik, MD – New York, NY
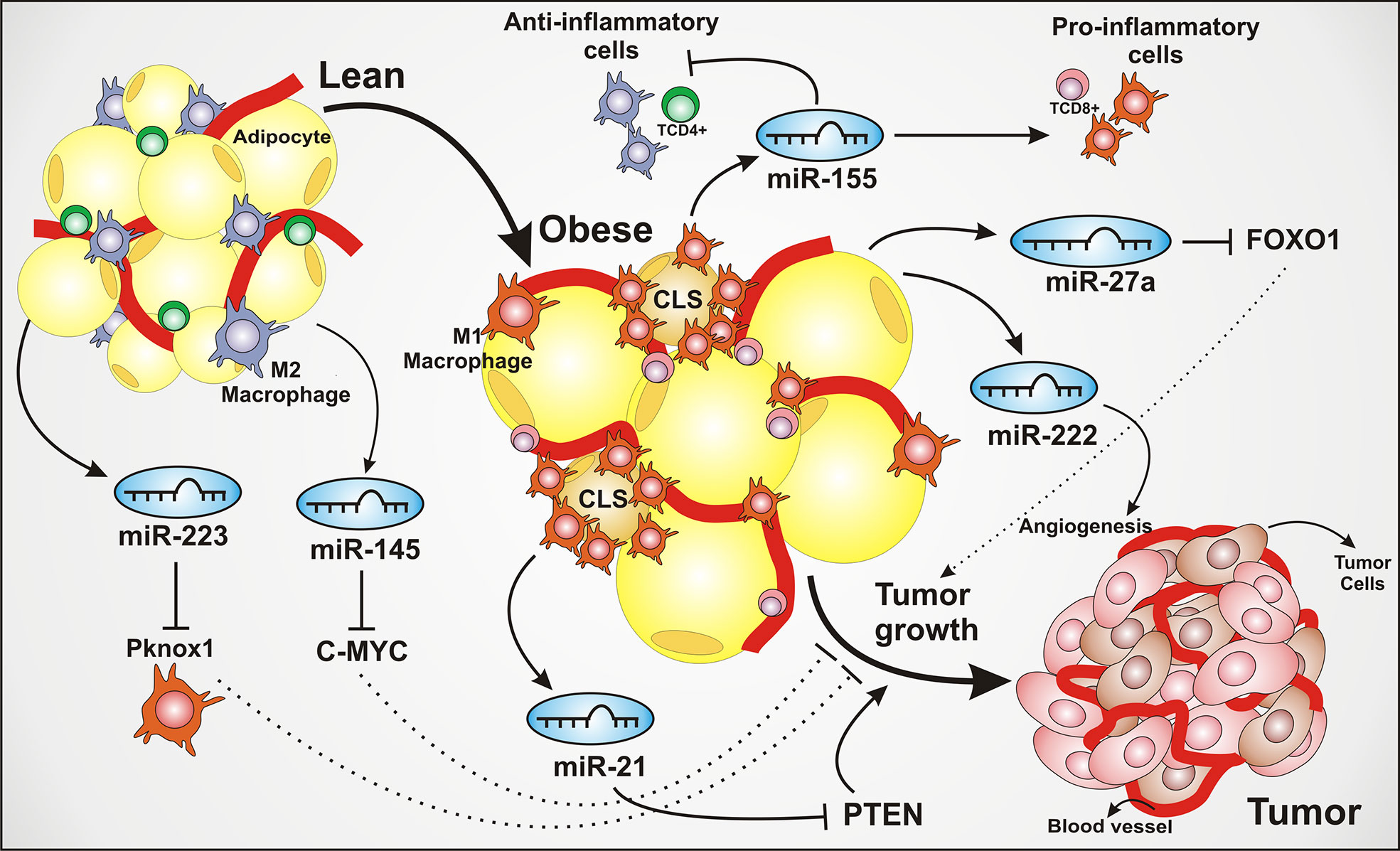
Frontiers The Impact of Adipose Tissue–Derived miRNAs in Metabolic Syndrome, Obesity, and Cancer

The impact of obesity on adipocyte-derived extracellular vesicles

An Endothelial-to-Adipocyte Extracellular Vesicle Axis Governed by Metabolic State. - Abstract - Europe PMC
PF-4708671 rapidly increased AMPK phosphorylation before inhibiting

High doses of EVs activate lysosomal and repress membrane trafficking

Adipose Tissue: Physiology to Metabolic Dysfunction - Endotext - NCBI Bookshelf

Krumsiek, Jan

Dr. Paul Paik, MD – New York, NY
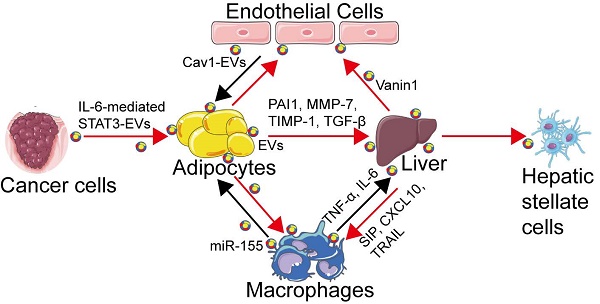
Current understanding of the role of Adipose-derived Extracellular Vesicles in Metabolic Homeostasis and Diseases: Communication from the distance between cells/tissues
Anatomy of the female human breast. The human breast consists of
The Human Breast Cell Atlas – world's most comprehensive single-cell atlas of healthy breast tissue
 Reebok Apparel Men Classic Colorblock Reversible Puffer Jacket PURE GR – Reebok Canada
Reebok Apparel Men Classic Colorblock Reversible Puffer Jacket PURE GR – Reebok Canada YEOREO Ultimate Workout Crop Tops for Women Long Sleeve Open Back
YEOREO Ultimate Workout Crop Tops for Women Long Sleeve Open Back International yoga day poster design Royalty Free Vector
International yoga day poster design Royalty Free Vector Spot Rust Cushion Cover, Rust Pillow Cover
Spot Rust Cushion Cover, Rust Pillow Cover Anyone else's trackers and speed-ups fit weird? : r/lululemon
Anyone else's trackers and speed-ups fit weird? : r/lululemon smooth wireless push up bra
smooth wireless push up bra