Full agonists, partial agonists and inverse agonists
4.6 (250) In stock
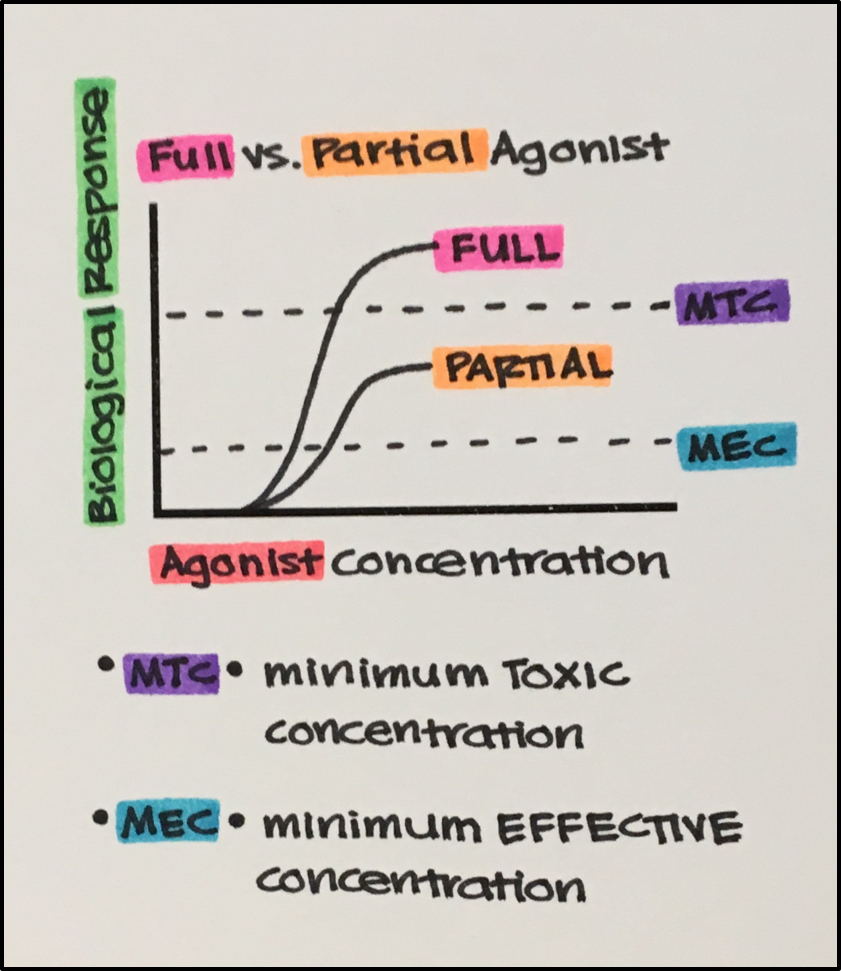
An agonist is a ligand that binds to a receptor and alters the receptor state resulting in a biological response. A full agonist reaches the maximal response capability of the system, and a partial agonist does not (even at full receptor occupancy). A partial agonist acts as an antagonist in the presence of a full agonist (if they compete for the same receptors). An inverse agonist is a ligand that by binding to receptors reduces the fraction of them in an active conformation. Spare receptors are said to exist wherever a full agonist can cause a maximum response when occupying only a fraction of the total receptor population.

Figure 2 from Inverse agonism: the classic concept of GPCRs revisited [Review].

2.Mechanism of drug actons
8. Two Main Classes of Receptor Ligands in Pharmacology: Agonists & Antagonists – Principles of Pharmacology – Study Guide

inverse agonist
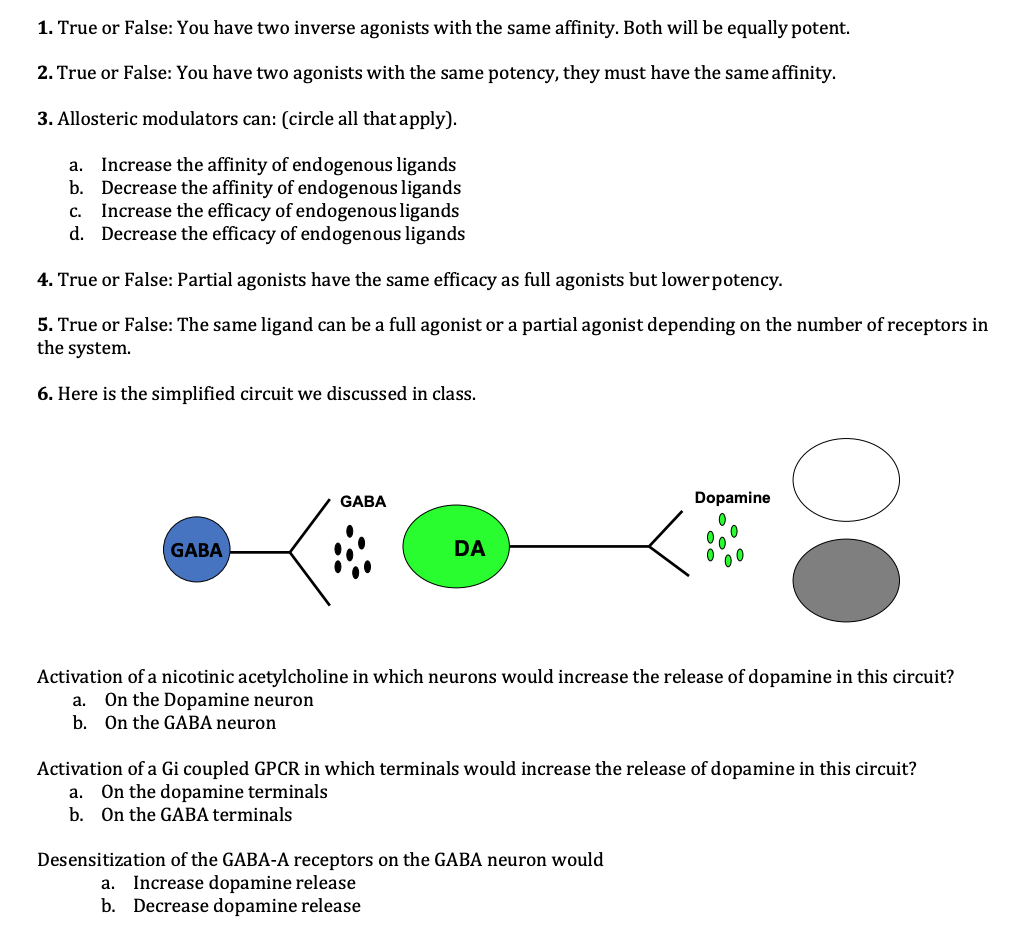
Solved 1. True or False: You have two inverse agonists with

Rational drug design of CB2 receptor ligands: from 2012 to 2021 - RSC Advances (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/D2RA05661E

Drug Receptor Binding - an overview

Agonists and antagonists

20 Partial Agonist Images, Stock Photos, 3D objects, & Vectors

3 H]GTP formation from [ 3 H]GDP and NTP in S49 wild-type (wt)

Agonist, Antagonist, Partial Agonist, Inverse Agonist

How to understand from the L*R graph, do we deal with agonist, antagonist and inverse agonist - Quora

Agonism and antagonism - Physics, Pharmacology and Physiology for Anaesthetists
Full Effect 04 All-Over Nourishing Mousse , 8.5 Oz
Memecoin season is in FULL EFFECT. This is your WARNING! Be safe
- Ralph Lauren Solid Molded Cup Bralette Bikini Top & Solid Taylor Hipster Bikini Bottom
 2 New pairs of Cuddl Duds Warm Layer Leggings, small. 2 times the money. Total price is quantity times bid price. - Rocky Mountain Estate Brokers Inc.
2 New pairs of Cuddl Duds Warm Layer Leggings, small. 2 times the money. Total price is quantity times bid price. - Rocky Mountain Estate Brokers Inc. Molinete De Pesca Marine Sports Prisma 3000 - 5 Rolamentos - Recolhimento 5.2:1 - C3 Pesca & Aventura
Molinete De Pesca Marine Sports Prisma 3000 - 5 Rolamentos - Recolhimento 5.2:1 - C3 Pesca & Aventura White color Cotton Flex fabric for Women's Kurti Palazoo - Charu
White color Cotton Flex fabric for Women's Kurti Palazoo - Charu- Women's Leggings for sale in Hyderabad, Facebook Marketplace
- Sofia Vergara Reveals New Season of Walmart Line With Amazing Pics


