High body temperature increases resistance to
4.6 (195) In stock
Viral infections affect the elderly more frequently than the younger population. Moreover, elderly individuals also have lower mean body temperatures. Taking cues from these clinical observations, a team of researchers from The University of Tokyo undertook a study to find the missing link between body temperature and infection resistance. Findings indicate that increased body temperature suppresses virus replication and excessive inflammatory responses.
Elevated temperature inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication in respiratory epithelium independently of IFN-mediated innate immune defenses
Elevated temperature inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication in respiratory epithelium independently of IFN-mediated innate immune defenses

Experiments in infant mice suggest new way to prevent spread of flu in people

Newborn piglets serve as a model for studying influenza
Elevated temperature inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication in respiratory epithelium independently of IFN-mediated innate immune defenses

Low levels of ionizing radiation exposure : r/biology

免疫」なくして人類なし!免疫の不思議/人間だって動物だもの~人獣共通感染症~, 連載
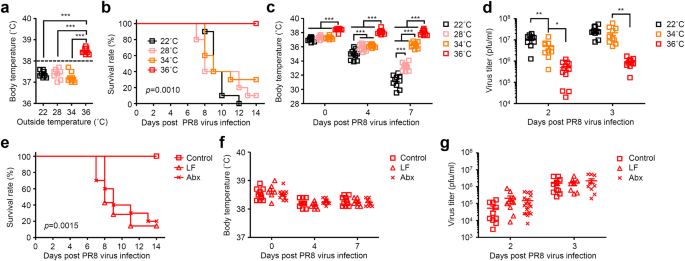
High body temperature increases gut microbiota-dependent host resistance to influenza A virus and SARS-CoV-2 infection
Elevated temperature inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication in respiratory epithelium independently of IFN-mediated innate immune defenses

THE INSTITUTE OF MEDICAL SCIENCE, THE UNIVERSITY OF TOKYO
Elevated temperature inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication in respiratory epithelium independently of IFN-mediated innate immune defenses
Charlotte's 'Juicy Body Goddess,' viral TikTok sensation offering plus-size options
Viruses that are commonly found in the human body. MB−virus
Adolescents with HIV in Zimbabwe are not being told why an undetectable viral load matters
Infographic: The Havoc SARS-CoV-2 Wreaks on the Body
Florida auto shop goes viral on TikTok thanks to a giant cat
 G308 Fully PaDDed Wirefree Bra Size 38B, Black
G308 Fully PaDDed Wirefree Bra Size 38B, Black Traditional Chinese Style Yoga Wear Dance Costume
Traditional Chinese Style Yoga Wear Dance Costume Musuos Women Deep V-neck Robes Lace Sheer Nightgown Full-Length Long Night Dress
Musuos Women Deep V-neck Robes Lace Sheer Nightgown Full-Length Long Night Dress AND1 Men's Pro Platinum Boxer Briefs, 6 Pack, 6
AND1 Men's Pro Platinum Boxer Briefs, 6 Pack, 6 Lucky Me! Go Cup Mini Batchoy 40g – Marilen Mini Mart
Lucky Me! Go Cup Mini Batchoy 40g – Marilen Mini Mart- Visionary Printed Pants
