Comment on: Proposal for a new diagnostic classification of
4.6 (521) In stock
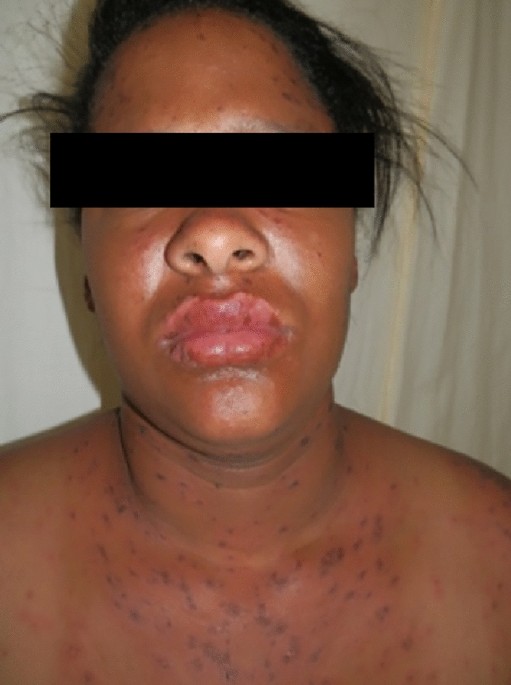
Stevens–Johnson syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), and SJS/TEN overlap (SJS/TEN), collectively referred to SJS/TEN, form a spectrum of severe life-threatening adverse drug reactions whose pathomechanism is not fully understood. The article "Photodistributed Stevens–Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: A Systematic Review and Proposal for a New Diagnostic Classification" by McKinley et. al., discusses a distinct distribution of epidermal necrosis in SJS/TEN, attributable to preceding exposure to ultraviolet radiation (UVR), and relative sparing of photo-protected areas. After reviewing numerous cases within the Immune-mediated Adverse drug Reactions in African HIV endemic setting Register and Biorepository (IMARI-SA) at the University of Cape Town with a similar clinical pattern as those published by McKinley et. al., we propose that the relative sparing of some areas giving an impression of photo-distribution is due to localised increase in skin pressure that reduces the blood supply in that area below a critical threshold. A dip in blood supply below this critical threshold quantitively limited T lymphocytes and cytokines that drive SJS/TEN to reach and damage the skin.

Sites in The Gambia (left) and Kenya (right).

Parameter means separated by C. difficile infection outcomea

Biobank sample workflow. Residual samples are biospecimens that are
PDF) Comment on: Proposal for a new diagnostic classification of photodistributed Stevens–Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis

Advanced field laboratory setup used for Ebola virus disease outbreak

Procedures for Remnant Biospecimen Investigation in Sepsis (REMISE)

Sites in The Gambia (left) and Kenya (right).

Comment on: Proposal for a new diagnostic classification of photodistributed Stevens–Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis, European Journal of Medical Research

PDF) Comment on: Proposal for a new diagnostic classification of photodistributed Stevens–Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis

Study Selection Process to Identify Cases of Photodistributed

Sites in The Gambia (left) and Kenya (right).

Georg Amun Hofmann's research works Medical University of Vienna, Vienna (MedUni Vienna) and other places

Procedures for Remnant Biospecimen Investigation in Sepsis (REMISE)

Mean posterior probabilities from combined traces (circles) for C.

Mean posterior probabilities from combined traces (circles) for C.
Brassière fille 8 ans - 10 ans blanc hetm - H&M - 8 ans
Sara Little Turnbull Inspired the N95 Respirator From a Bra Cup Design
Mrs sadie hi-res stock photography and images - Alamy
Kari Traa Sol Bra - Seconde main Brassière de sport - Blanc - M / Light Support
 Signature Lace Low Rise Thong – Mixology
Signature Lace Low Rise Thong – Mixology Wireless Push Up Bra Cotton Underwear Women AB Cup Bra Gathered Comfort V Brassiere Push Up Lingerie Bralette
Wireless Push Up Bra Cotton Underwear Women AB Cup Bra Gathered Comfort V Brassiere Push Up Lingerie Bralette Floral Applique Satin Cami Wedding Dress in 2023
Floral Applique Satin Cami Wedding Dress in 2023- READY STOCK ] Lovaria So Fit Series Nursing Bra (Front Open Clip)
 AURORA 15 Filodoro pantythose - Boutique Isla Mona
AURORA 15 Filodoro pantythose - Boutique Isla Mona BROOKS, Elizabeth 'Bunty' Anne - Obituary - Barrie - Barrie News
BROOKS, Elizabeth 'Bunty' Anne - Obituary - Barrie - Barrie News
