Developing a Thermodynamical Method for Prediction of Activity
4.6 (210) In stock
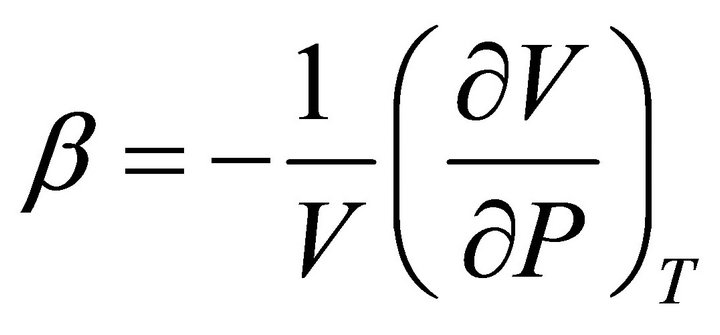
Results of the experimental measurements on the partial molar volume of kerosene used as a medium for dissolving TBP are utilized to determine the activity of TBP in the binary kerosene-TBP solution through the application of Gibbs-Duhem equation. The treatment is based on combination of the experimental data with the thermodynamic values available on the compressibility factor of pure kerosene at room temperature. It is shown that the activity of TBP in kerosene has a positive deviation from ideality with an activity coefficient derived as follows:1) at X TBP ≤ 0.01: γ TBP = 42.530, 2) at the 0.01 X TBP 0.2: 3) at the higher TBP concentrations 0.2 X TBP 0.97: and 4) at TBP Raoultian concentrations 0.97 ≤ X TBP:γ TBP = 1. These quantities can be utilized at temperature closed to 298 K.

PDF) Developing a Thermodynamical Method for Prediction of Activity Coefficient of TBP Dissolved in Kerosene

Thermodynamic modelling - Wikipedia

Experimental and Thermodynamic Investigation on CO2 Absorption in Aqueous MEA Solutions

Comparison between activity coefficient of the test data that

McCabe-Thiele plot for stripping of manganese loaded D2EHPA using 180

PDF) Thermodynamics of extraction of Zn2+ from sulfuric acid media with a mixture of DEHPA and MEHPA
Drug design - Wikipedia

PDF) Developing a Thermodynamical Method for Prediction of Activity Coefficient of TBP Dissolved in Kerosene

E. ALAMDARI, Professor (Associate), PhD, Amirkabir University of Technology, Tehran, TUS, Department of Mining and Metallurgical Engineering

PDF) Thermodynamics of Prediction
States of Matter

Eskandar Keshavarz Alamdari - Academia.edu
Compressibility Factor Calculator
Compressibility factor (gases) - Knowino





