Dermatology for the practicing allergist: Tinea pedis and its
4.5 (587) In stock
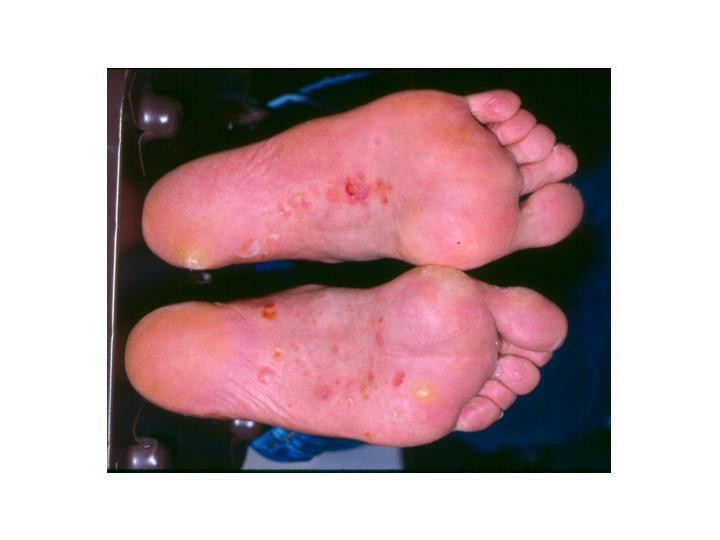
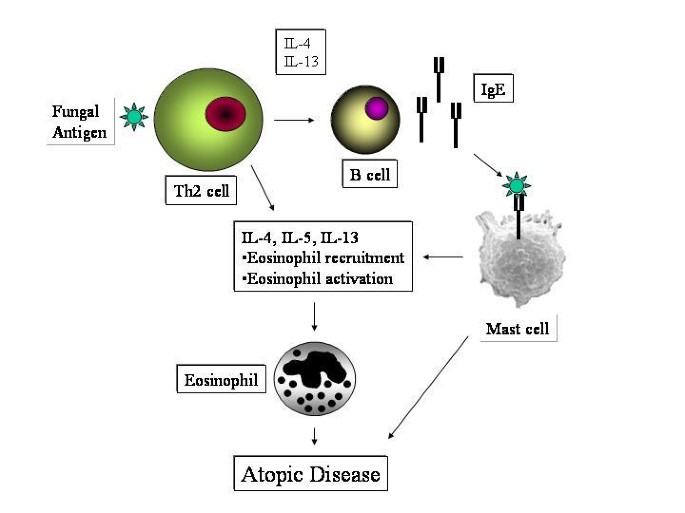
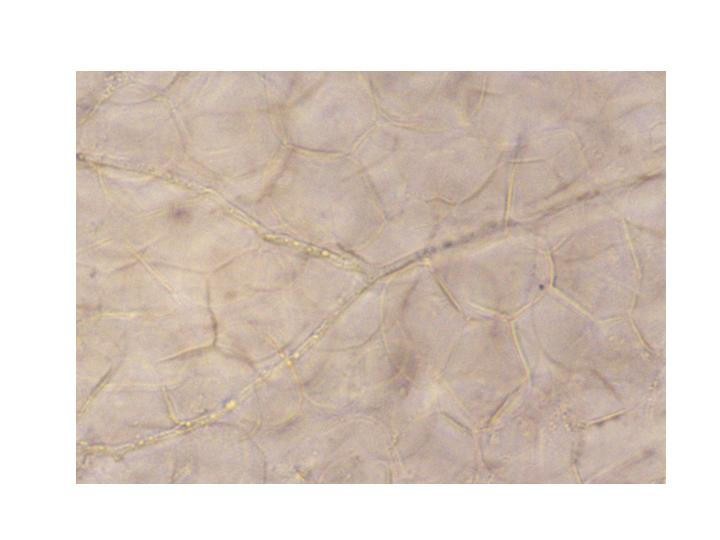
Tinea pedis is a chronic fungal infection of the feet, very often observed in patients who are immuno-suppressed or have diabetes mellitus. The practicing allergist may be called upon to treat this disease for various reasons. Sometimes tinea infection may be mistaken for atopic dermatitis or allergic eczema. In other patients, tinea pedis may complicate allergy and asthma and may contribute to refractory atopic disease. Patients with recurrent cellulitis may be referred to the allergist/immunologist for an immune evaluation and discovered to have tinea pedis as a predisposing factor. From a molecular standpoint, superficial fungal infections may induce a type2 T helper cell response (Th2) that can aggravate atopy. Th2 cytokines may induce eosinophil recruitment and immunoglobulin E (IgE) class switching by B cells, thereby leading to exacerbation of atopic conditions. Three groups of fungal pathogens, referred to as dermatophytes, have been shown to cause tinea pedis: Trychophyton sp, Epidermophyton sp, and Microsporum sp. The disease manifests as a pruritic, erythematous, scaly eruption on the foot and depending on its location, three variants have been described: interdigital type, moccasin type, and vesiculobullous type. Tinea pedis may be associated with recurrent cellulitis, as the fungal pathogens provide a portal for bacterial invasion of subcutaneous tissues. In some cases of refractory asthma, treatment of the associated tinea pedis infection may induce remission in airway disease. Very often, protracted topical and/or oral antifungal agents are required to treat this often frustrating and morbid disease. An evaluation for underlying immuno-suppression or diabetes may be indicated in patients with refractory disease.
Dermatology for the practicing allergist: Tinea pedis and its complications, Clinical and Molecular Allergy
Dermatology for the practicing allergist: Tinea pedis and its complications, Clinical and Molecular Allergy

Inflammation and vesicles on a wrestler's feet- Clinical Advisor
Exaggerated Immune Reaction to Trichophyton Fungus Results in an Inflammatory Tinea Pedis

Tinea pedis: not just the curse of the athlete - BPJ65 December 2014

Exploring Essential Oils in the Treatment of Tinea Pedis – Naturopathic Doctor News and Review
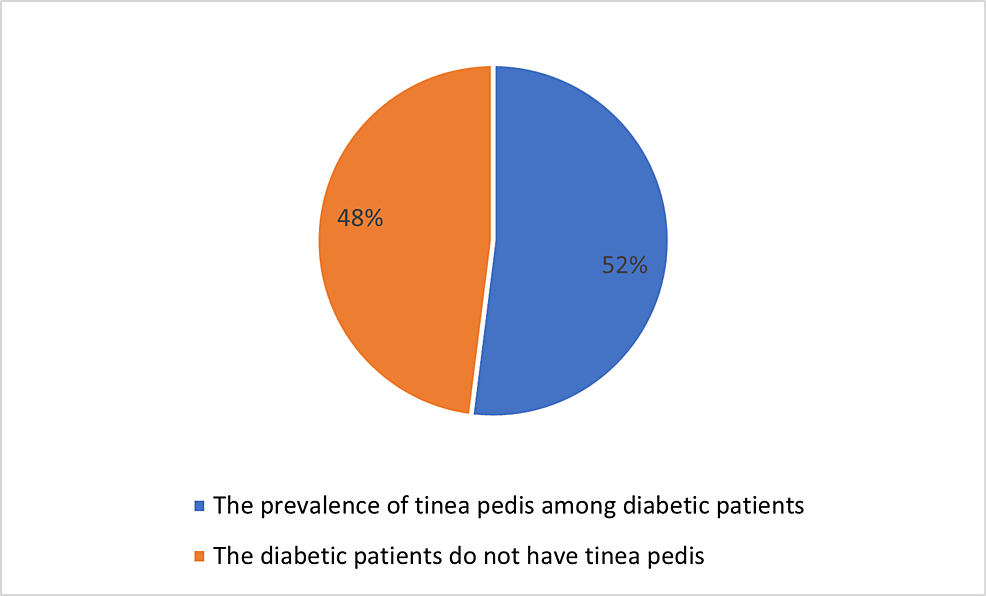
Cureus, Prevalence and Factors Associated With Tinea Pedis Among Diabetic Patients in Saudi Arabia: A Descriptive Cross-Sectional Study

A machine learning‐based, decision support, mobile phone application for diagnosis of common dermatological diseases - Pangti - 2021 - Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology - Wiley Online Library
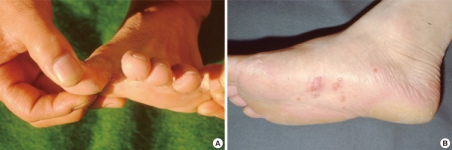
PMC3924009_jkms-29-272-g005.png

Id reactions (syn. ide reactions; autoeczematisation)
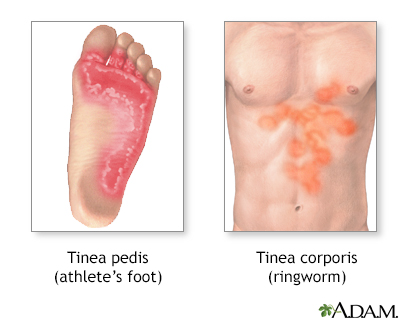
Ringworm Information Mount Sinai - New York

Dermatophyte Infection: What Is It, Causes, Signs and Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, and More

PDF) Tinea pedis: The etiology and global epidemiology of a common fungal infection

Chapter 42: Fungal Skin Infections, Handbook of Nonprescription Drugs: An Interactive Approach to Self-Care, 20th Edition
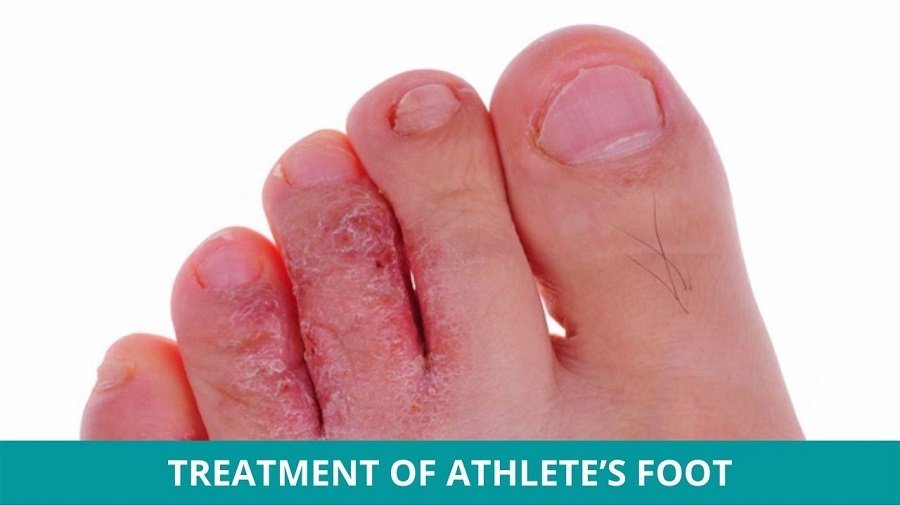
What is the most effective treatment for athlete's foot?
This is Tinea Pedis aka. Athletes - Sault Chiropody Clinic
File:Tinea pedis 1319.jpg - Wikimedia Commons
Tinea pedis moccasin type - Altmeyers Encyclopedia - Department





