The role and therapeutic potential of stem cells in skeletal
4.9 (543) In stock
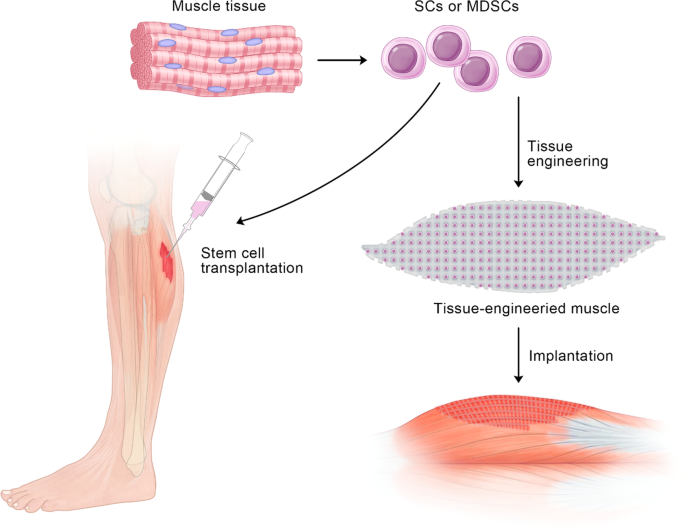
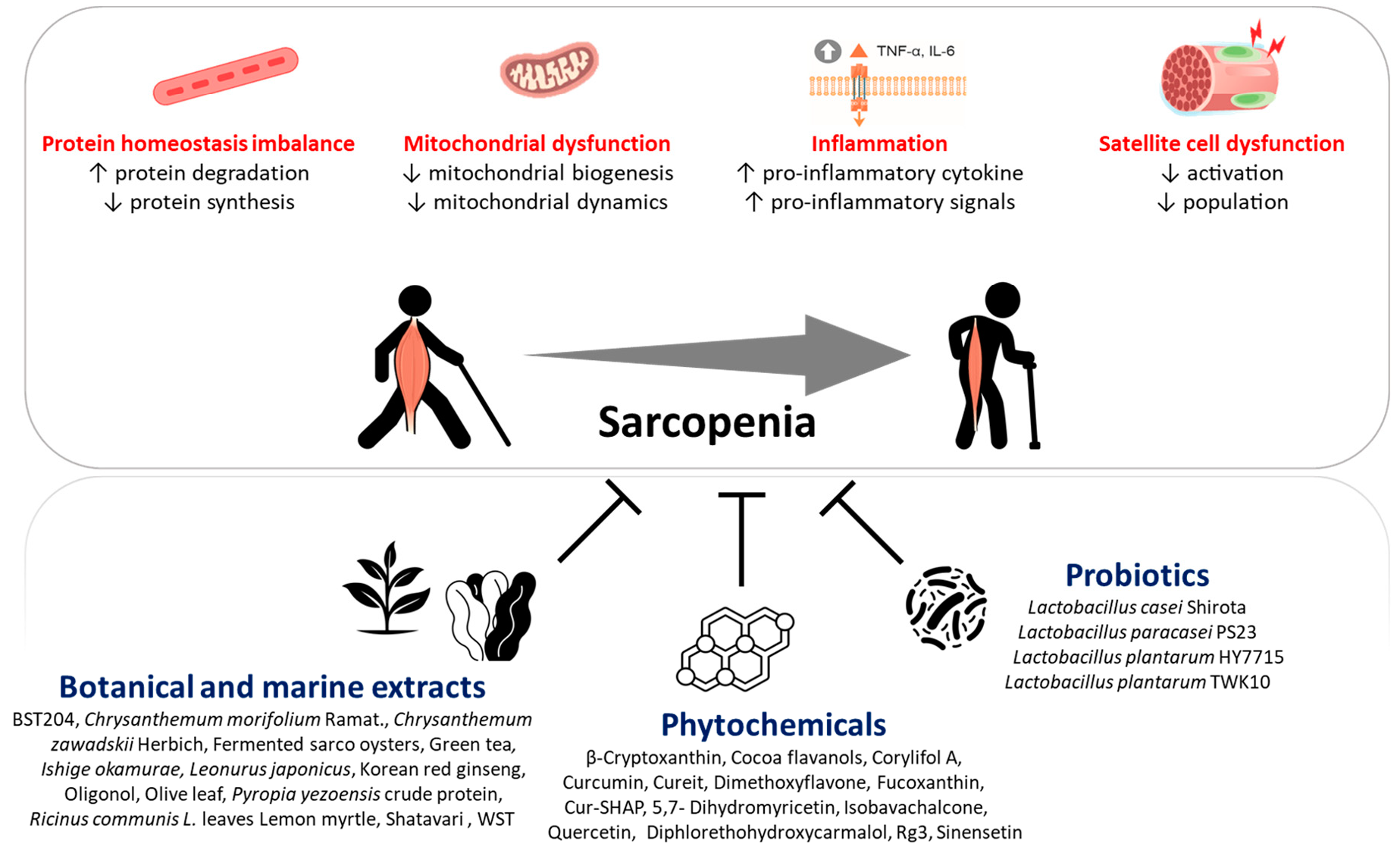
Sarcopenia is a common age-related skeletal muscle disorder featuring the loss of muscle mass and function. In regard to tissue repair in the human body, scientists always consider the use of stem cells. In skeletal muscle, satellite cells (SCs) are adult stem cells that maintain tissue homeostasis and repair damaged regions after injury to preserve skeletal muscle integrity. Muscle-derived stem cells (MDSCs) and SCs are the two most commonly studied stem cell populations from skeletal muscle. To date, considerable progress has been achieved in understanding the complex associations between stem cells in muscle and the occurrence and treatment of sarcopenia. In this review, we first give brief introductions to sarcopenia, SCs and MDSCs. Then, we attempt to untangle the differences and connections between these two types of stem cells and further elaborate on the interactions between sarcopenia and stem cells. Finally, our perspectives on the possible application of stem cells for the treatment of sarcopenia in future are presented. Several studies emerging in recent years have shown that changes in the number and function of stem cells can trigger sarcopenia, which in turn leads to adverse influences on stem cells because of the altered internal environment in muscle. A better understanding of the role of stem cells in muscle, especially SCs and MDSCs, in sarcopenia will facilitate the realization of novel therapy approaches based on stem cells to combat sarcopenia.
Skeletal muscle differentiation of human iPSCs meets

Maintaining bovine satellite cells stemness through p38 pathway
Nutrients, Free Full-Text

Stem-cell therapy for cardiac disease

Stem Cell Therapy: Overview, Benefits & Risks (2024)

Postconditioning for salvage of ischemic skeletal muscle from reperfusion injury: efficacy and mechanism

Autophagy regulates cytoplasmic remodeling during cell reprogramming in a zebrafish model of muscle regeneration. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Expression of skeletal muscle (red), ion channel (green), smooth muscle
IJMS, Free Full-Text
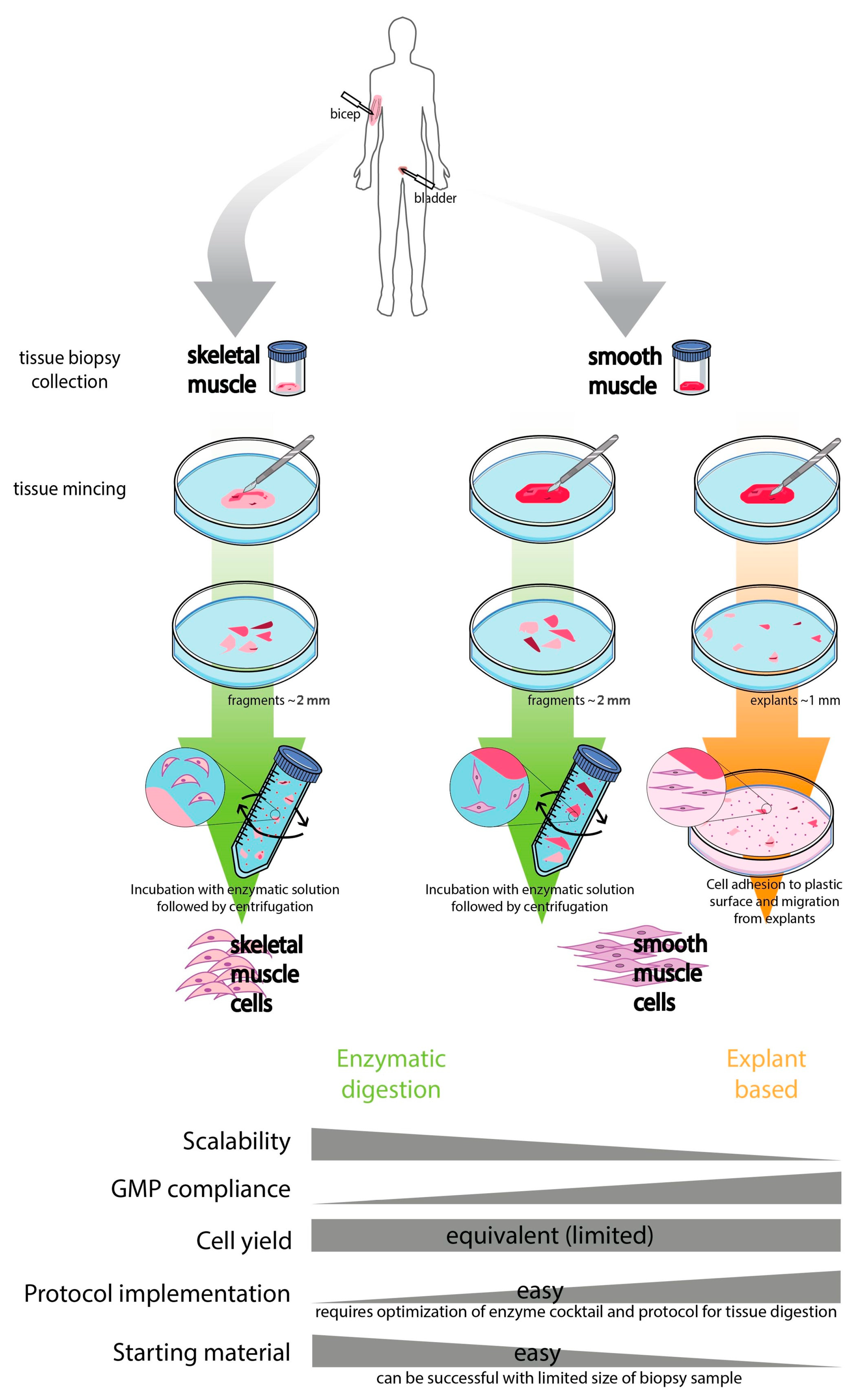
Bioengineering, Free Full-Text
Decrease in the expression of muscle-specific miRNAs, miR-133a and miR-1, in myoblasts with replicative senescence

Cell‐Based Therapies For Degenerative Musculoskeletal, 60% OFF

PDF] Potential Therapies Using Myogenic Stem Cells Combined with

PDF) Biomedical applications of muscle-derived stem cells: from bench to bedside
CrossFit Muscle Damage for Size and Strength?
Diastasis Recti Repair and Tummy Tuck Surgery - Miguel Delgado, MD
Bioengineering, Free Full-Text
Should You Take Collagen for Muscle Recovery & Repair?
Weight Loss Tips: Soreness After A Workout? Try Eating These Foods For Faster Recovery
 White male senior citizen hi-res stock photography and images - Alamy
White male senior citizen hi-res stock photography and images - Alamy Sleep Top
Sleep Top- Goodnites Girls' Size S/M Nighttime Bedwetting Underwear, 44 ct - Fry's Food Stores
 Hello kitty couple CK cartoon underwear outer wear cartoon animation cute cute suspender elastic underwear sports bra set gift - AliExpress
Hello kitty couple CK cartoon underwear outer wear cartoon animation cute cute suspender elastic underwear sports bra set gift - AliExpress Knee pad - Wikipedia
Knee pad - Wikipedia Hello my love concept Stock Photo
Hello my love concept Stock Photo
