SARS-CoV-2 spike protein promotes inflammatory cytokine activation
4.6 (347) In stock
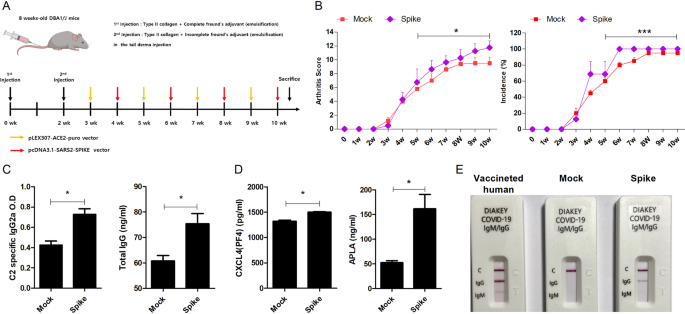
Background Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) induces inflammation, autoantibody production, and thrombosis, which are common symptoms of autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis (RA). However, the effect of COVID-19 on autoimmune disease is not yet fully understood. Methods This study was performed to investigate the effects of COVID-19 on the development and progression of RA using a collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) animal model. Human fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) were transduced with lentivirus carrying the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein gene in vitro, and the levels of inflammatory cytokine and chemokine expression were measured. For in vivo experiments, CIA mice were injected with the gene encoding SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, and disease severity, levels of autoantibodies, thrombotic factors, and inflammatory cytokine and chemokine expression were assessed. In the in vitro experiments, the levels of inflammatory cytokine and chemokine expression were significantly increased by overexpression of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in human FLS. Results The incidence and severity of RA in CIA mice were slightly increased by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in vivo. In addition, the levels of autoantibodies and thrombotic factors, such as anti-CXC chemokine ligand 4 (CXCL4, also called PF4) antibodies and anti-phospholipid antibodies were significantly increased by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Furthermore, tissue destruction and inflammatory cytokine level in joint tissue were markedly increased in CIA mice by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Conclusions The results of the present study suggested that COVID-19 accelerates the development and progression of RA by increasing inflammation, autoantibody production, and thrombosis. Video Abstract
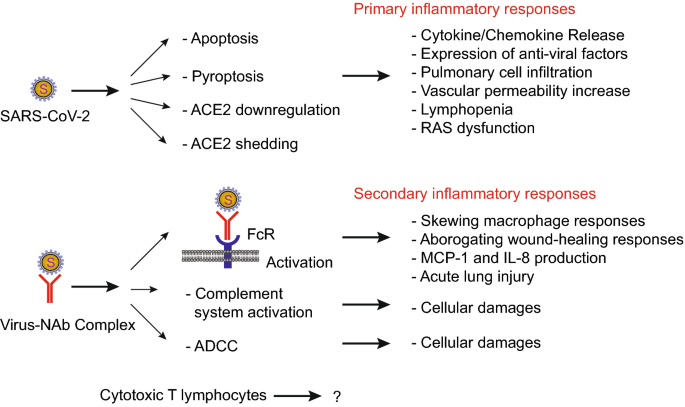
Understanding SARS-CoV-2-Mediated Inflammatory Responses: From Mechanisms to Potential Therapeutic Tools
-1.jpg)
SARS-CoV-2 spike stimulates hyperinflammation via Toll-like receptor 2
SARS-CoV-2 spike protein promotes IL-6 trans-signaling by activation of angiotensin II receptor signaling in epithelial cells

PDF] Immunotherapy of Autoimmune Diseases with Nonantibiotic

FOXP3 Antibody PE 12-5773-82 from Thermo Fisher Scientific
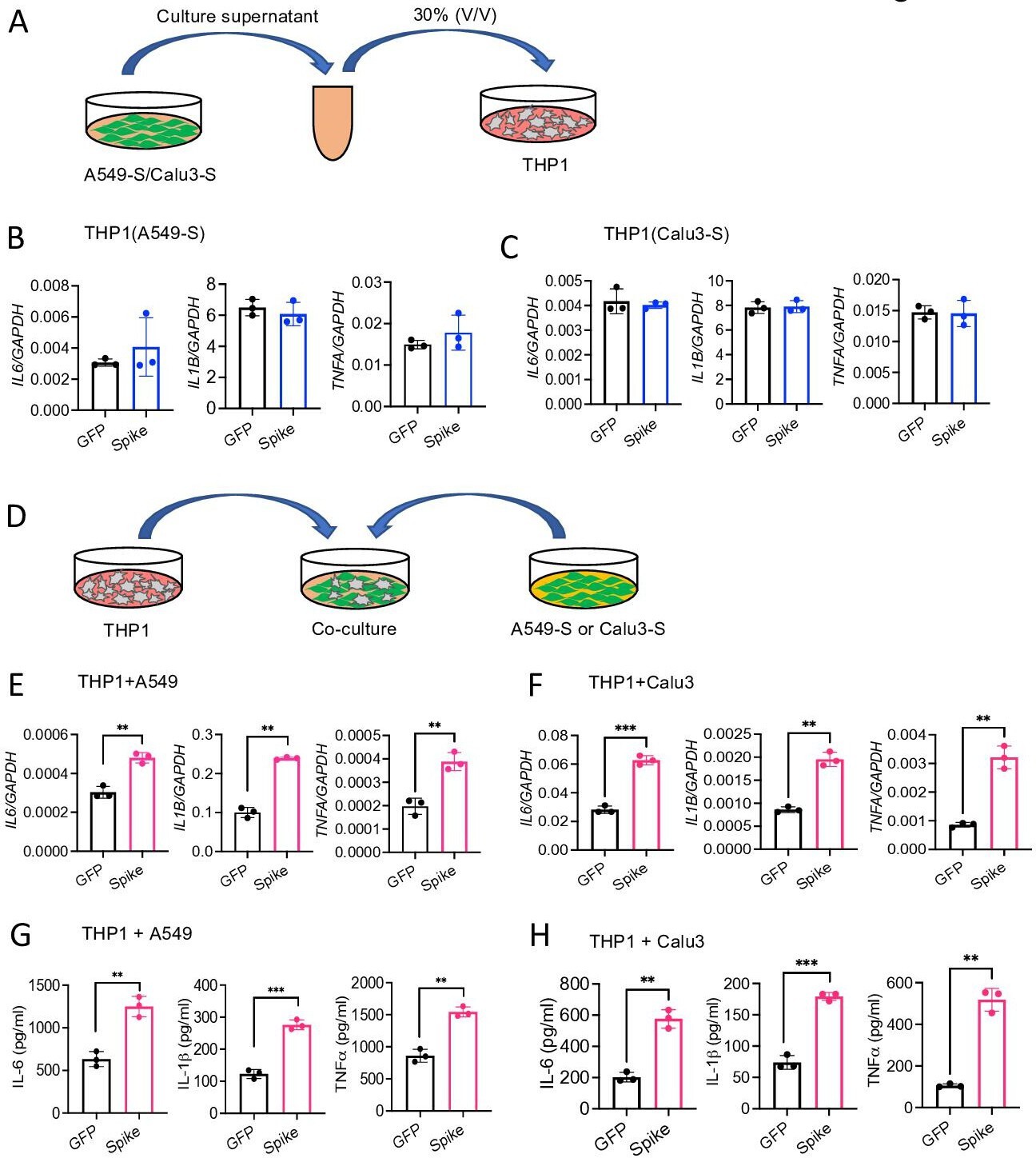
SARS-CoV-2 spike protein induces inflammation via TLR2-dependent activation of the NF-κB pathway
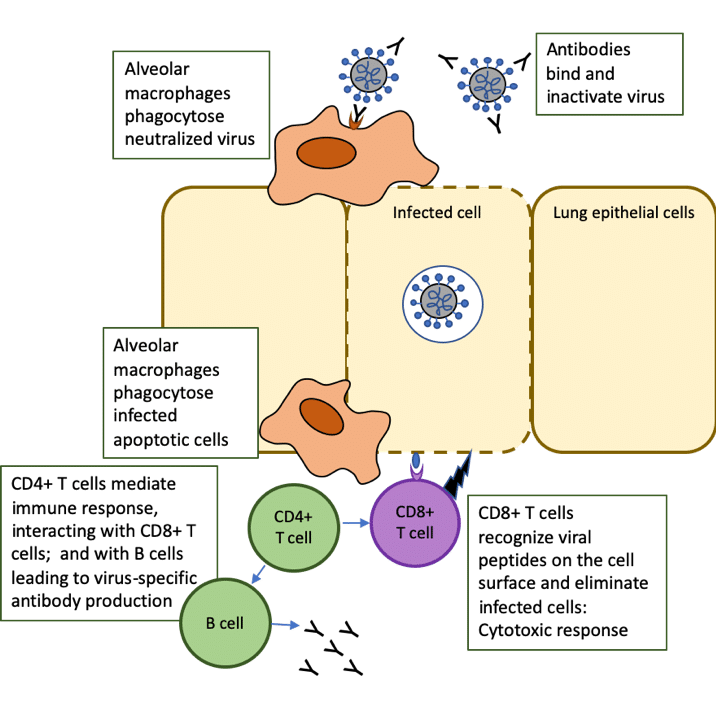
What is the role of T cells in COVID-19 infection? Why immunity is about more than antibodies - The Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine
The Glycan Ectodomain of SARS-Cov-2 Spike Protein Modulates Cytokine Production and Expression of CD206 Mannose Receptor in PBMC Cultures of Pre- COVID-19 Healthy Subjects[v1]

APC anti-mouse CD25 102012 from BioLegend

Mechanisms for the nonantibiotic activities of minocycline and
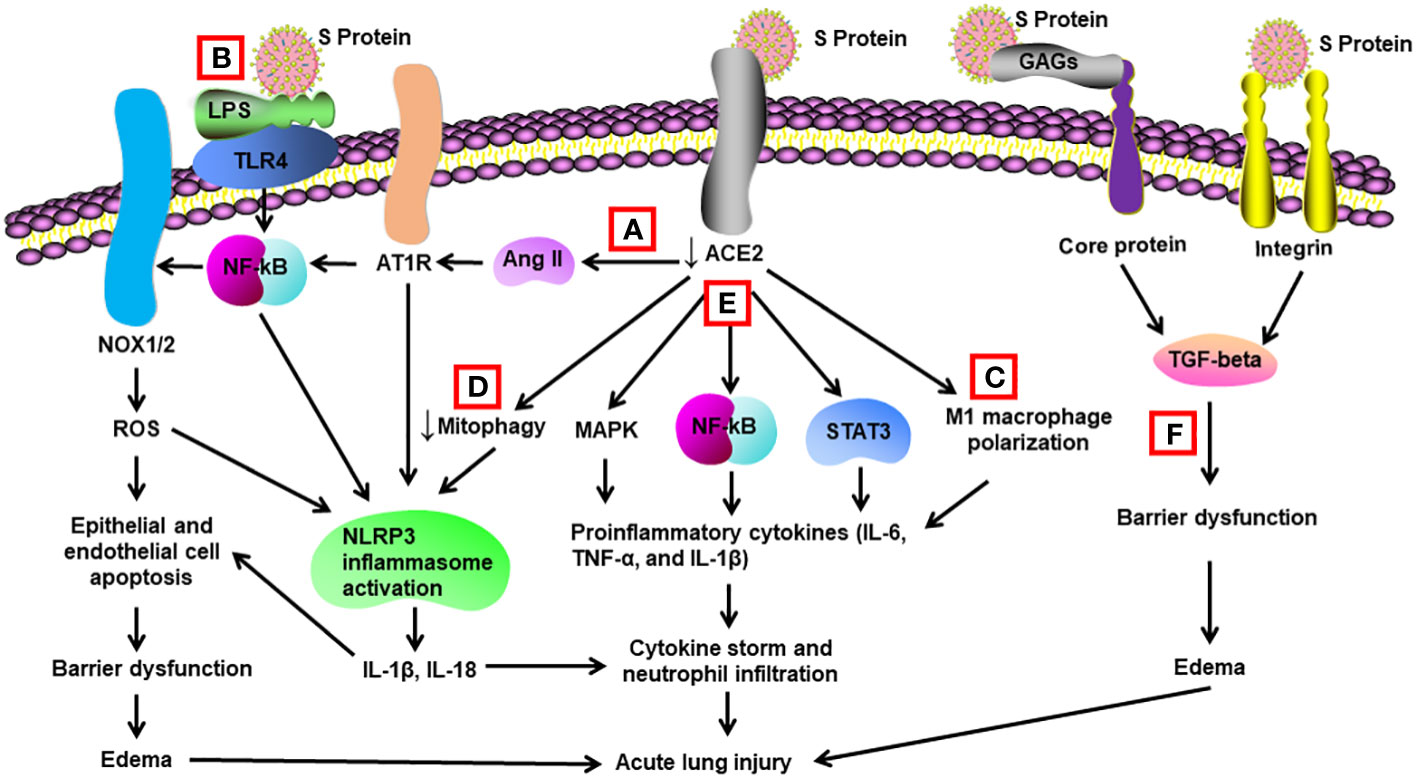
Frontiers Multifaceted role of SARS-CoV-2 structural proteins in lung injury

SARS-CoV-2 spike protein expressing epithelial cells promotes senescence associated secretory phenotype in endothelial cells and increased inflammatory response

SARS-CoV-2 Spike S1 glycoprotein is a TLR4 agonist, upregulates ACE2 expression and induces pro-inflammatory M1macrophage polarisation - Abstract - Europe PMC

CD4 Monoclonal Antibody (RM4-5), Super Bright™ 436 (62-0042-82)
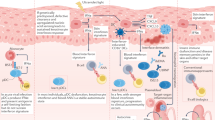
Type I interferons: crucial participants in disease amplification
Spike Name Meaning Drinks Mat Coaster Blue
Spike Barriers at Rs 300000/piece, Tyre Killer in Gurgaon
 Setis Strappy Sports Bra - Burgundy
Setis Strappy Sports Bra - Burgundy Women's Pajamas, Women's Nightwear
Women's Pajamas, Women's Nightwear BZB Kawaii Anime Cute Pajamas Set for Women Sweet Lovely Velvet Tube Top and Shorts Two Piece Cartoon Sleepwear Sets Black at Women's Clothing store
BZB Kawaii Anime Cute Pajamas Set for Women Sweet Lovely Velvet Tube Top and Shorts Two Piece Cartoon Sleepwear Sets Black at Women's Clothing store ERES Sportswear for Women sale - discounted price
ERES Sportswear for Women sale - discounted price Freya Womens Chi Underwire Idol Moulded Balcony Bra, 30F, Charcoal
Freya Womens Chi Underwire Idol Moulded Balcony Bra, 30F, Charcoal 10 Best Large Printable Number 11 PDF for Free at Printablee Large printable numbers, Printable numbers, Large printable
10 Best Large Printable Number 11 PDF for Free at Printablee Large printable numbers, Printable numbers, Large printable