Converting Wi-Fi signals to electricity with new 2-D materials, MIT News
4.6 (557) In stock
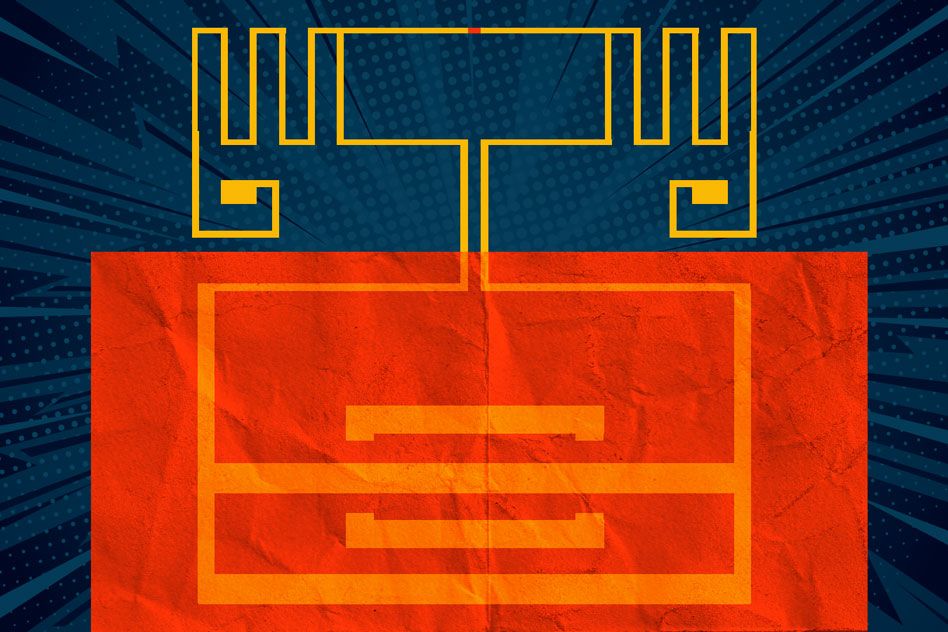
Researchers from MIT’s Microsystems Technology Laboratories have developed a fully flexible device made of the 2-D material molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) that converts energy from Wi-Fi signals into electricity to power electronics, wearables, internet-of-things technologies, and to charge batteries.
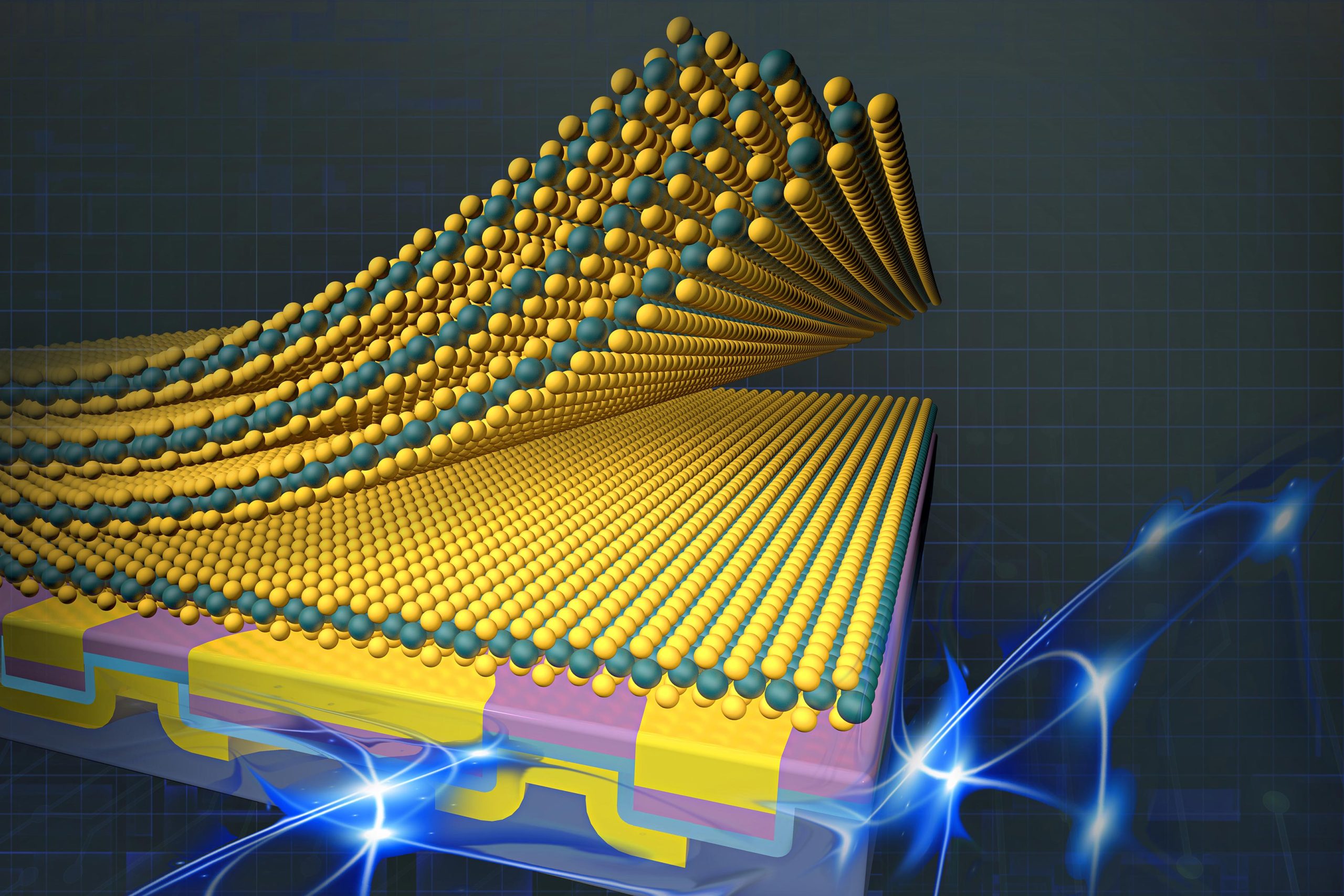
Next-Gen Electronics Transformed: MIT's 2D Integration Breakthrough

Solar and Wind Power Could Ignite a Hydrogen Energy Comeback
Nanomaterials, Free Full-Text

Yes, we have enough materials to power the world with renewable

MIT's new sensor can power itself without a battery
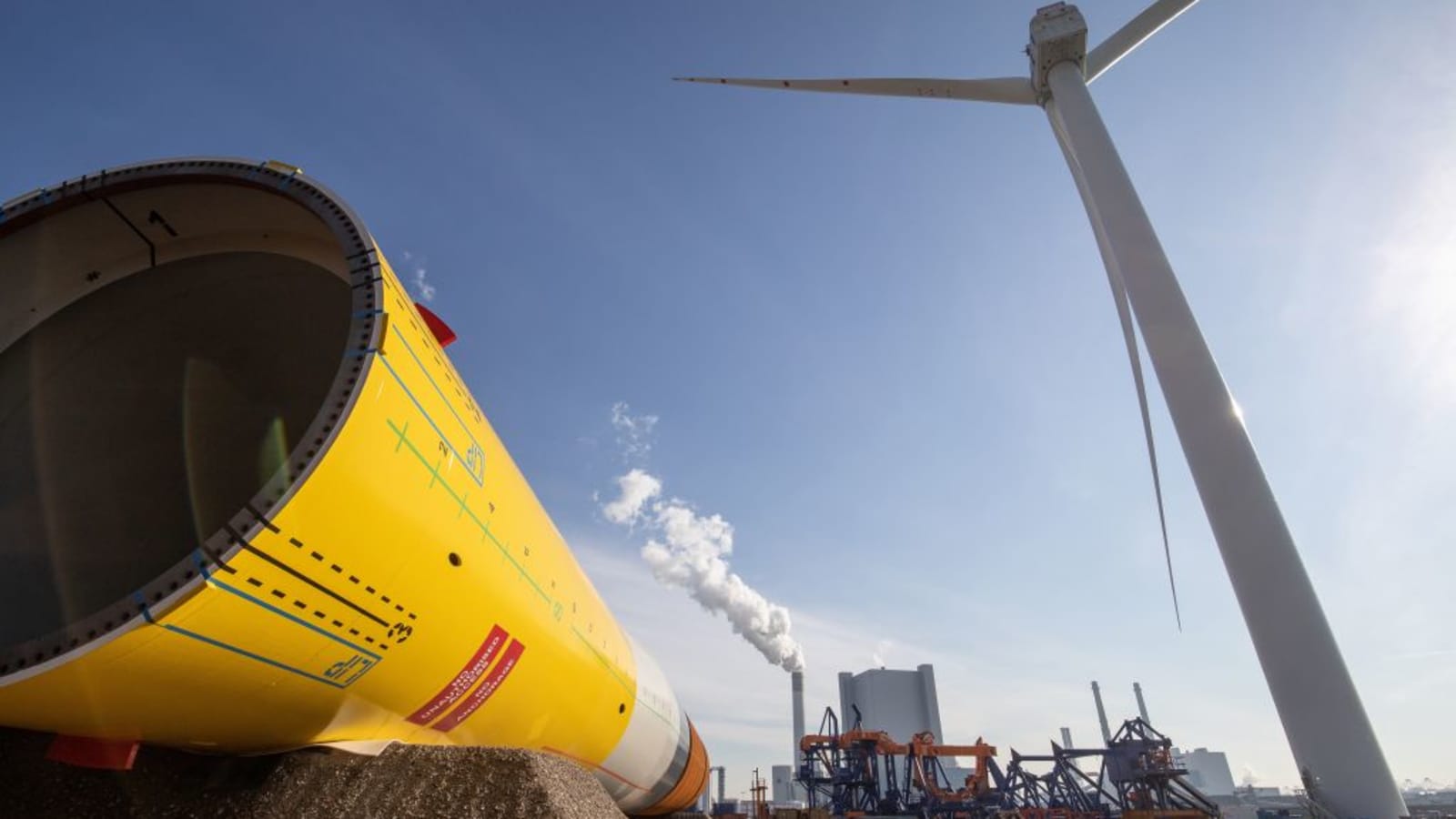

Green energy: The race to roll out 'super-sized' wind turbines is on
Frontiers Applications and Techniques for Fast Machine Learning

Carbon Footprint of the Internet Over Time Since 1990 (With Graphics)

Converting Wi-Fi Signals to Electricity with New 2-D Materials

Researchers safely integrate fragile 2D materials into devices

News Tomas Palacios

Access the Latest in Vision AI Model Development Workflows with

Researchers Use Cheap Wi-Fi Routers to Detect Human Posture

Converting Wi-Fi signals to electricity with new 2-D materials

Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text
Easy Tips to Troubleshoot Actiontec 7200 Wi-Fi Extender
Kinetic Switch Canada Wireless Light Switch Kitchener
Easy Tips to Troubleshoot Beacon 6 Gateway Connectivity
Enerj WS1024 1 Gang Wireless Kinetic Switch
Kinetic by Windstream Picks RouteThis to Drive WiFi for Home - TelecomDrive
 PEACH JUMPSUIT SCRUBS – CyTy
PEACH JUMPSUIT SCRUBS – CyTy MİSTİRİK Panax Model Sports Corset Bustier Anti-Sagging Tight Bustier Corset Corset Bra Black Color - Trendyol
MİSTİRİK Panax Model Sports Corset Bustier Anti-Sagging Tight Bustier Corset Corset Bra Black Color - Trendyol Buy Danskin Women's Essentials Ankle Legging, Black, Small at
Buy Danskin Women's Essentials Ankle Legging, Black, Small at Taupe Ribbed Cropped Camisole Tank Top
Taupe Ribbed Cropped Camisole Tank Top Tall Bearded Iris (Iris 'Iced') in the Irises Database
Tall Bearded Iris (Iris 'Iced') in the Irises Database Zuwimk Bras For Women Plus Size,Women's Bras Molded Cup Seamfree
Zuwimk Bras For Women Plus Size,Women's Bras Molded Cup Seamfree