Associations of body shapes with insulin resistance and
5 (800) In stock
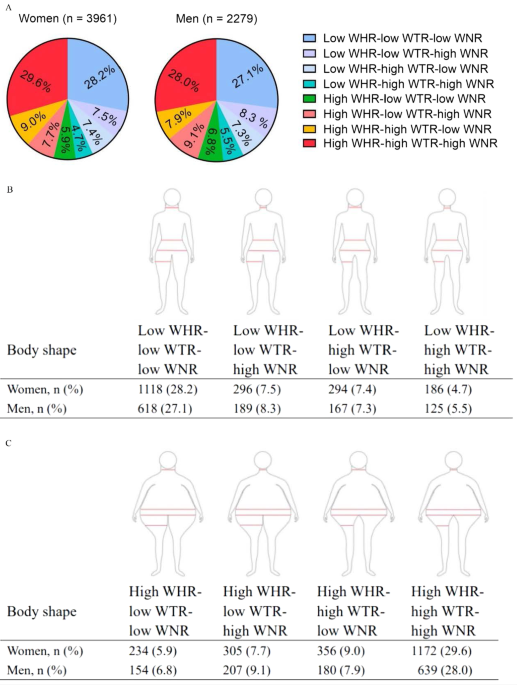
Background We aimed to define refined body shapes by using multiple anthropometric traits that represent fat distribution, and evaluate their associations with risk of insulin resistance (IR) and cardiometabolic disorders in a Chinese population. Methods We performed a cross-sectional analysis in 6570 community-based participants aged ≥ 40 years. Four body circumferences (neck, waist, hip, and thigh) and their ratios were put simultaneously into an open-source Waikato Environment for Knowledge Analysis platform to select the worthiest indicators in determining IR. The ratio of the top 3 fat distribution indicators was used to define the refined body shapes. Results We defined 8 distinct body shapes based on sex-specific combinations of waist-to-hip ratio (WHR), waist-to-thigh ratio (WTR), and waist-to-neck ratio (WNR), which differed in participants’ distribution and risk of IR and related cardiometabolic disorders. In women, as compared to the low WHR-low WTR-low WNR shape, all body shapes were significantly associated with IR and related cardiometabolic disorders; while in men, the low WHR-high WTR-high WNR shape and the higher WHR related shapes were significantly associated with IR and related cardiometabolic disorders. Stratified by WHR, the results were consistent in women; however, no significant associations were detected in men. Conclusions We defined 8 distinct body shapes by taking WHR, WTR, and WNR, simultaneously into account, which differed in association with the risk of IR and related cardiometabolic disorders in women. This study suggests that body shapes defined by multiple anthropometric traits could provide a useful, convenient, and easily available method for identifying cardiometabolic risk.

Comprehensive genetic study of the insulin resistance marker TG:HDL-C in the UK Biobank

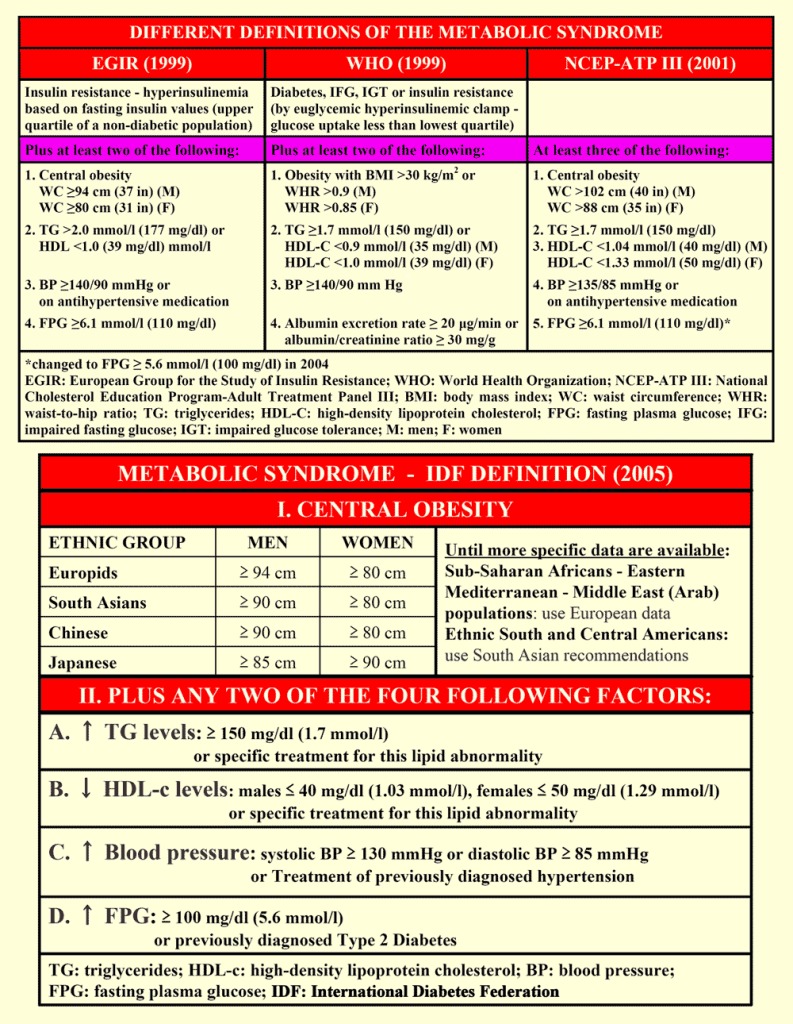
PDF] Does the Additional Component of Calf Circumference Refine Metabolic Syndrome in Correlating With Cardiovascular Risk?

Associations of body shapes with insulin resistance and cardiometabolic risk in middle-aged and elderly Chinese, Nutrition & Metabolism
Clinical Problems Caused by Obesity - Endotext - NCBI Bookshelf
Mid-Arm Circumference and All-Cause, Cardiovascular, and Cancer Mortality among Obese and Non-Obese US Adults: the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey III

Performance of RunEntropy biomarkers for the diagnosis of MetS (a) and

PDF) Association of TNF-α with insulin resistance in Type 2 diabetes mellitus

Performance of RunEntropy biomarkers for the diagnosis of MetS (a) and

PDF) Association of neck circumference-related indices with metabolic, atherogenic and liver function biomarkers in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a cross-sectional study

Relation of plasma ceramides to visceral adiposity, insulin resistance and the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus: the Dallas Heart Study

The dietary requirement for total sulfur amino acids in adults aged ≥60 years appears to be higher in males than in females - The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition
There is really a single ideal body shape for women?
Dressing Your Body: The Average Man
How much the average woman's body shape has changed
Body shape expectations of women seeking laparoscopic sleeve
 Bluemaple 6 Pack Copper Compression Socks For Women And Men Circulation-Best Support For Medical
Bluemaple 6 Pack Copper Compression Socks For Women And Men Circulation-Best Support For Medical Women's ColdGear Authentic Leggings
Women's ColdGear Authentic Leggings as-is* Perfectly Thrashed Double Knee Carhartt Workwear Pants
as-is* Perfectly Thrashed Double Knee Carhartt Workwear Pants Artisanal Wall-Mount Candleholder
Artisanal Wall-Mount Candleholder 100+] Leon Brawl Stars Wallpapers
100+] Leon Brawl Stars Wallpapers Calvin Klein Womens CUStomized Lift Bra : Buy Online at Best Price in KSA - Souq is now : Fashion
Calvin Klein Womens CUStomized Lift Bra : Buy Online at Best Price in KSA - Souq is now : Fashion